THE IMPORTANCE OF DEVELOPING AN INFORMATION SYSTEM System Development is compilation of new system to replace or repair which have system (old system). Things causing the importance of developing an information system, that is:
1. Existence of Problems to generated by other old system, that is:
· Old system is not all right and that result the system can’t work better
· Development of organization cause must that organization development a new system. For example requirement of broader information.
2. To Reach opportunities
In market emulation, speed of information or time efficiency has very determining successful
3. Existence of directives
Compilation of new system can happen because the directives from the boss or from outside organization. For example: regulation of government.
THE PURPOSE OR GOAL OF DEVELOPING AN INFORMATION SYSTEM
1. Solving problems
2. Reach for opportunity
3. Following instruction
THE ORGANIZATION’S EXPECTATIONS AFTER IMPLEMENTING AN INFORMATION SYSTEM
The happen of some improvement a new System effect of its growth. The improvement that is:
1. Performance
New System can improve of performance and Measured to use throughput and response time
2. Information
Improvement of information presented quality, this matter can prevent of information which of no use. For example: terrorizing. Because system there isn't mistaking, so user can got more accurate information
3. Economy
Improvement to advantage or benefit and decreasing cost
4. Control
Improvement to operation so can detected insincerity and repair mistake.
5. Efficiency
Improvement of operational Efficient, for example replacement of sales (SPG) usage with making of advertisements for good promotion in media print and electronic
6. Services
Give Improvement of system service. For example in payment of tax or making SIM using system will more is watering down of governmental institution to serve society.
PRINCIPLES OF DEVELOPING AN INFORMATION SYSTEM
1. Developing an Information System to management
When developing system must to be seen that using this system is management, so that system have to fulfill requirement management supporting.
2. Developing an Information System is a big investment
Investigation of all alternative to determine best alternative, most beneficial and also to minimize missing cost opportunity. Best investigation must to be valuable with the meaning beneficial and useful of cost-benefit analysis & cost-effectiveness can be used to determine value a project.
3. Developing an Information System need educated people.
Educated people mean must not formal education, but can be conducted on the job training.
4. Step work and duty performed within system development
Process system development usually need step work and team work. Schedule is very needing to efficacy and accuracy of system development.
5. Process System development do not have to massage
Process with other process can be conducted concurrently according to requirement
6. Don't fear to cancel a project
Decision to continue or canceled a project must to be evaluate with carefully in order to generate loss.
7. Documentation of system
Documentation of System can be used as by communications materials between user and system analyst.
SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIVE CYCLE MODELS
1. WATERFALL MODEL
This model is first model that is around 1970 year. This model conduct systematically approach and massage start from requirements level go to design, implementation, testing / verification, and maintenance. Referred as waterfall because the phase for the shake of phase passed by must wait to finish of previous him phase and successively walk.

Picture above is a step of waterfall model. this is Following clarification of conducted phases in this model :
· Requirements.
Process of required initial which requirement by user, for example interface user, etc.
· Design.
This process used to change requirements above become representation into "blueprint" software before started coding. Design must to earn implementation requirement
· Implementation.
To can understand by machine, in this case is computer, so mentioned design have to be turned into program pass process of coding.
· Verification.
Made something must be test to be avoid from error, and him result must really as according to requirement.
· Maintenance.
Conservancy is very need by system in order that can precise function and exact of target.
Advantages waterfall model
· Testing is inherent to every phase of the waterfall model
· It is an enforced disciplined approach
· It is documentation driven, that is, documentation is produced at every stage
Disadvantages waterfall model
· It only incorporates iteration indirectly, thus changes may cause considerable confusion as the project progresses.
· As The client usually only has a vague idea of exactly what is required from the software product, this WM has difficulty accommodating the natural uncertainty that exists at the beginning of the project.
· The customer only sees a working version of the product after it has been coded. This may result in disaster if any undetected problems are precipitated to this stage.
2. ITERATIVE MODEL
In iterative model there are initial of planning before planning remain to afterwards can be defined by wanted requirement, the requirements then analysis by analyst system and made by design interface design, afterwards of implementation. Testing must be done to the test of system to be free from error, and result him have to really as according to requirement. Evaluate system is excess from this model, this is conducted to evaluate the system until the system really perfect.

· Initial planning
We can starting planning process or initial requirement system or define idea to start of system development.
· Planning
Planning is a thinking that ripe to system development.
· Requirement,
Process of required initial which requirement by user, for example interface user, etc.
· Analysis and design
In this process system analyst analysis everything the system need. And can Planning of design such as: interfaces, data structure, etc.
· Implementation
In Implementation process can mentioned design have to be turned into program pass process of coding.
· Testing
In this process can testing system and its application. Analysis mistake of system and check all system application.
· Evaluation
In Process evaluation can be repair process, maintenance and renewal towards development system.
· Deployment
Process deployment can distribution system to public so that develop can know deficit of system.
3. SPIRAL MODEL
Spiral model proposed initially by Boehm. Spiral model divided to be 4 areas, that is:
· Determine objectives
In determine objective can do requirement plan process
· Identify and resolve risk
in this process can do identification process, planning and analyze risks may be happen. In identification and planning process, we must defined, requirement, time precision, and information to help a process development. In risk analysis can do analysis to risks may be happen.
· Development and test
In Development process can do engineering process, construction and testing to development system. In testing can do testing process to make of system.
· Plan the next iteration
In his process can do iteration process to plan evaluation in the event of request from customer in order to change to system.

From picture, process started from unidirectional peripatetic core with clock needle encircle spiral. First trajectory of rotation is requirement of concept also determine operation of concept, afterwards continue to requirement plan where this process is done to be elaborated by requirements of planning, before continue to process of verification and validation have to pass analysis risk afterwards then to development plan where in this process The Plan is a contract between the Project Manager, Executive Sponsor, Project Team and other management of the enterprise associated with and/or affected by the project. Each Project Plan component is essentially a work product resulting from subtasks in the Make Plan Project Management task, but can be revised during other project management activities. Return of rotation at process of risk analysis than verification and validation last test plan and back to analysis risk. Phase hereinafter represent prototype operational which its process of design detailed, code, integration, test and implementation last after all process finish hence release system.
APPROACHES OF DEVELOPING A SYSTEM
1. Classical approach versus structured approach
Classical approach is approaches which following step of system life circle without supplied by tool and adequate technique. The Problems which emerge at classical approach, that is:
· Development of software become difficultly
· Expense of system care and maintenance become expensive
· Possibility happened a big mistake
· Successful a system less well guarantee.
· Internal issue of applying system
Structured approach provided with techniques and tools which required in development of system until the result of system can be defined better.
2. Piecemeal approach versus System approach
Piecemeal approach is system development approach which emphasize at a activity or certain application. While System Approach will attention information system as a unity integrated to the each activity.
3. Buttom-up approach versus Top Down approach
Buttom-up approach started from under level of organization (level operational where transaction done). While Top Down approach started from upper level of organization (planning strategy level)
4. Total System approach versus Modular approach
Total System approach is a approach to develop of system at a time by totally. While Modular approach can try prevented of system become to simple some part.
5. Gread loop approach versus Evolutionary approach
Gread loop approach to totally apply change at a time to use sophisticated technology. While Evolutionary approach can apply sophisticated of technology just needed application.
THE MEANING OF METHODOLOGY, METHOD AND ALGORITHM
What is methodology?
Methodology is methods to used in science
What is method?
Method is a stile of systematic to do something
What is algorithm?
Algorithm is medley of procedure to analyst a problem
THE THREE CLASSIFICATIONS OF DEVELOPMENT METHODOLOGY
1. Functional decomposition methodologies
Emphasize resolving of system become easier subsystem so that to easy understand, design and applied. For example: HIPO, Stepwise refinement or iterative stepwise refinement, information hiding
2. Data-oriented methodologies
Processed emphasize of characteristic data. And can be grouped to two groups, that is:
o Data-flow oriented methodologies (this methodology relied on resolving of system into modules pursuant to data type).
For example: SADT (Structured analysis and design techniques), Composite Design, and SSAD (Structured system analysis and design)
o Data-structure oriented methodologies (this methodology is emphasizing input and output structure).
For Example: JSD (Jackson’s systems development) and W/O (Warnier / Orr).
3. Prescriptive methodologies
It’s usually provided by factory maker of software.
For example:
o ISDOS (information system design and Optimization system) is developing software in university of Michigan. ISDOS used to automatic of system information development process.
o PLEXSYS used to do transformation of high level computer language to code executable configuration hardware.
o PRIDE is good software to design/analysis system, data management, and documentation.
o SDM/70 (System development methodology / 70) is a software containing method, estimation, documentation and guide of administration to helped user development to take care of system.
o SPECTRUM is a development methodology of system which developer by SII (Spectrum International. Inc.)
o STES (Software requirement Engineering system) and SREM (Software requirement Engineering methodology).
o And other prescriptive methodologies. For example: Chapin’s approach, DBO, PAD, HOS, MSR, and PDL
TOOLS FOR DEVELOPING A SYSTEM
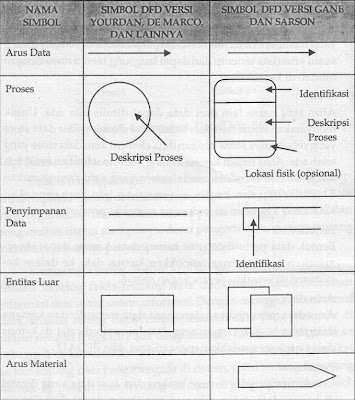
Tools used in a general methodology in the form of picture, graph or diagram. Tools of system development in form of Graph type, that is:
· HIPO Diagram, used in HIPO methodology and others methodology.
· Data Flow Diagram, used in structure system analysis and design methodology.
· Structured Chart, used in structure system analysis and design methodology.
· SADT diagram, used in SADT methodology
· Warnier/Orr Diagram, used in Warnier/Orr methodology
· Jackson’s diagram, used in Jackson’s system development methodology
Tools of System Development in Form Draft:
1. Activity charting
· System flowchart
· Program Flowchart(program logic flowchart and detailed computer program flowchart)
· Paperwork flowchart or form flowchart
· Database relationship flowchart
· Process flowchart
2. Layout charting
3. Personal relationship charting
· organization chart
· working distribution chart
TECHNIQUES USED IN DEVELOPING A SYSTEM
1. Management project technique can use to project schedule
For Example: CPM (Critical Path Method) and PERT (Program evaluation and Review Technique)
2. Technique of find a fact can used to collect and determine data / fact (interview, observation, questionnaires ,and sampling )
3. Cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness analysis
4. Technique to meeting
5. walkthrough technique
THE DIFFERENCES OF BEING A SYSTEM ANALYST AND A PROGRAMMER
System analyst is a people to analyst system or study problems and determine requirement of user to identify correct resolve. Duty Analyst System to connect difference of knowledge between user and programmer. Which Programmer is a people to write code program appropriate of design analyst system.
Responsibility and duty of programmer and system analyst
| Programmer | system analyst |
| Responsibility of programmer just on making a computer program. | Responsibility of system analyst just not on making a computer program but on all system. |
| Knowledge of programmer on technology computer, system computer, and language program. | Knowledge of system analyst must vast on this handle area. |
| Duty of programmer have technique characteristic and must exact for do program instructions. | Duty of system analyst is make a program but just limited in trouble-shooting marginally |
| Duty of programmer is not concerning many people but just limited with programmer and system analyst | Duty of system analyst is concerning with many people. |
THE KNOWLEDGE A SYSTEM ANALYST SHOULD PROCESS
1. Knowledge about data Processing technology, computer technology and computer programming.
o Skill of technical which must have by system analyst is using technique and tools for the software development.
o Knowledge technical which must have by system analyst is knowledge about hardware of computer, operating system, etc.
2. Business Knowledge in general used as communications medium with user. Knowledge about business is financial accounting, accountancy of management, system operation of management, marketing, production, personnel management, monetary, organizational staff, etc.
3. Knowledge of quantitative method. Such as: regression, linier programming, dynamic programming, network, decision tree, trend, etc.
4. Skill of complex resolving problem. System analyst must have skill to breaking problem and than stringing up the problem.
5. Skill of communication between staff.
6. Skill of constructed of relation between personnel.
TEAM SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT
1. Manager of system analyst
2. Lead system analyst
3. Senior system analyst
4. System analyst
5. Junior system analyst
6. Senior Application programmer
7. Application programmer
8. Junior Application programmer
Reference:
- http://lecturer.ukdw.ac.id/othie/softwareprocess.pdf
- Jogianto Hartono, Analisis & Desain Sistem Informasi. Edisi ke-3.Jogyakarta: Penerbit Andi, 2007